🖥️
What is BIOS? Beginner Guide
🔍 Introduction
In every computer,
there’s a small but very important system that works before your
operating system even starts. It’s called BIOS (Basic Input/Output System).
Whether you're a beginner or someone looking to understand how your PC boots
up, knowing BIOS is essential.
This guide will help you
understand:
- What is a BIOS?
- How it works
- Different types of BIOS
- How to access and configure BIOS
- Why is BIOS important
- And much more…
🧠
What is BIOS?
BIOS stands for Basic Input/Output System.
It is a firmware (software embedded in hardware) stored on a chip on
your computer's motherboard. When you turn on your computer, the BIOS is
the first software that runs.
🔧 It
initializes and tests your system hardware and loads the operating system
from a boot device (like your hard disk or SSD).
📌 Key Points:
- BIOS is stored in a ROM (Read-Only
Memory) chip
- It's independent of your operating
system
- It runs before any software or
apps
- Acts as a bridge between your hardware and OS
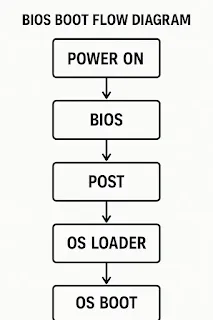
The BIOS follows a
sequence of steps every time the computer starts:
🔁
Step-by-step BIOS Process:
1.
🔋
Power is turned on
2.
🧪
BIOS runs POST (Power-On Self Test)
to check RAM, CPU, keyboard, etc.
3.
📦
BIOS initializes all connected hardware
4.
📂
It checks for a bootable device
(Hard Disk, USB, etc.)
5.
🚀
Loads the bootloader of the operating system
6. 💻 Hands over control to the OS
✅ Without BIOS, your computer wouldn’t know how to start
🧪
POST – Power On Self Test
When you press the power
button:
- BIOS performs a self-check
to ensure all hardware is functioning.
- This is called POST (Power-On Self
Test).
- If something is wrong (like faulty
RAM), BIOS will show error messages or beep codes.
🔔 POST is the first step of any computer startup process.
🧱
BIOS Structure: Key Components
BIOS is made of multiple
modules, each handling a different function:
🧩
Main Parts of BIOS:
1.
🧪 POST Module
– Tests basic hardware
2.
📟 CMOS Setup
Utility – Allows users to configure settings
3.
🧠 BIOS Drivers
– Provide low-level control over hardware
4.
🚀 Bootstrap
Loader – Loads the OS bootloader
🧰
BIOS Functions
Here are the main
functions of BIOS:
🔹
POST (Power-On Self Test)
🧪 Tests CPU,
RAM, keyboard, storage devices.
🔹
Boot Process Initiation
🚀 Loads
operating system from the selected boot device.
🔹
Hardware Initialization
🔧 Activates
video display, storage, input/output ports.
🔹
CMOS Settings Access
⚙️ Allows
configuration of boot order, system time, fan speed, voltage, etc.
🔹
Security Settings
🔒 Add passwords
to restrict BIOS access or system boot.
✅ BIOS ensures smooth coordination between hardware and software during startup.
🧾
CMOS and BIOS: What’s the Difference?
BIOS and CMOS are often mentioned together but
they’re different.
|
BIOS |
CMOS |
|
Firmware
in motherboard ROM |
Small
RAM chip powered by battery |
|
Controls
startup |
Stores
BIOS settings |
|
Cannot
be changed easily |
Settings
can be changed by user |
✅ CMOS battery keeps the BIOS settings
saved when the computer is off.
When you enter BIOS,
you’ll see a blue or black screen with several menus. Here's what you can
modify:
🛠️
Most Common BIOS Settings:
- 🗂 Boot Priority: Set which device (HDD, SSD, USB) the
OS should load from
- 🕒 System Time and Date: Set computer clock
- 🔒 Password Settings: Set BIOS or boot password
- 🌡️ Fan Control/Temperature Monitoring: Manage fan speeds and temperature
- 🧮 CPU/RAM Settings: Overclocking or enabling
virtualization
✅ Making the wrong changes here can
cause boot failure — change carefully!
You can access BIOS when
the system is first powered on.
⌨️ Common BIOS
Access Keys:
- F2
– (Acer, Dell, Asus)
- DEL
– (MSI, Gigabyte, ASRock)
- F10 or ESC – (HP, Lenovo)
📌 Press the key during the first 5
seconds after turning on the PC.
Modern computers no longer use the traditional BIOS system. Instead, they rely
on a more advanced system known as UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware
Interface) — offering better speed, more storage support, and enhanced
security.
🔍 Key
Differences Explained:
1.
Boot Support:
📌 Legacy BIOS supports only the MBR (Master
Boot Record) booting method.
📌 UEFI supports the more modern GPT (GUID
Partition Table), allowing better partition management and features.
2.
Disk Capacity:
📌 With BIOS, you’re limited to hard drives up to 2TB
in size.
📌 UEFI removes this limit and supports drives larger
than 2TB, which is essential for modern storage needs.
3.
Boot Speed:
📌 BIOS has a slower boot process due to its
outdated structure.
📌 UEFI enables a faster and more efficient boot,
saving you time every time you power on your PC.
4.
User Interface:
📌 BIOS features a text-only interface where you
navigate using the keyboard.
📌 UEFI comes with a graphical interface and even
allows you to use a mouse, making it easier to interact with settings.
5.
Security:
📌 BIOS lacks modern security measures like Secure Boot.
📌 UEFI includes Secure Boot, a feature that
prevents unauthorized software from loading during system startup — improving
overall security.
✅ UEFI is now standard for most modern systems.
🛠️
Should You Update BIOS?
BIOS can be updated, but
it’s risky and not often necessary.
📌
When to Update BIOS:
- 🔧 Adding support for new CPU or
hardware
- 🔐 Fixing serious bugs or security
issues
- ⚙️ Manufacturer recommends a critical
update
⚠️ Warning:
✅ A
wrong BIOS update can break your motherboard (brick it).
🧑💻 Always follow
official guides from your PC/motherboard manufacturer.
❗ Common BIOS Errors & Solutions
🔻
No Bootable Device Found
🔁
Check boot order in BIOS or reconnect drive
🔻
CMOS Battery Failure
🔋
Replace motherboard’s CMOS battery
🔻
BIOS Beep Codes
📣 Beep sounds
signal hardware issues like bad RAM or GPU.
Use your motherboard manual to decode the beeps.
🔋 Without
BIOS, your computer can’t start.
It tells your hardware how to work, checks for problems, and loads your OS.
🧠
BIOS is important because:
- Ensures compatibility between
components
- Helps diagnose errors
- Lets you tweak performance
- Secures system from unauthorized access
- 📖 Always read your motherboard manual
- ❌ Don’t change settings you don’t
understand
- 🔄 Back up important data before
updates
- 🔋 Replace CMOS battery every 3–5 years
- 🛡 Set a BIOS password if your system
is in public use
📅 BIOS was first
introduced in 1975 by Gary Kildall, creator of CP/M (an early OS).
🔄 IBM used it in the first personal computers in the
1980s.
Imagine you build a new
computer and plug everything in.
When you power it on, BIOS checks all components are working.
If RAM or storage is missing, it alerts you — before Windows even loads.
That’s why even modern
gamers and technicians often visit BIOS to set performance, enable
virtualization, or troubleshoot.
BIOS might seem
invisible, but it’s one of the most crucial parts of a computer.
From turning on your machine to starting the OS, BIOS handles everything
silently.
📝 Summary:
- BIOS stands for Basic Input/Output
System
- It initializes hardware and loads the
OS
- It includes POST, CMOS, drivers, and
bootstrap loader
- You can configure BIOS using access
keys like F2 or DEL
- UEFI is the modern replacement for
BIOS
- Be careful with BIOS updates and
settings





0 Comments